In May 2019, Botswana’s President Masisi justified the decision to recommence trophy hunting by emphasising that local communities will be guaranteed more than just menial jobs and enjoy sustainable wildlife management’s economic benefits.

As the passage of the Hunting Trophies (Import Prohibition) Bill moves to the Committee Stage of the House of Lords, a suite of amendments has been tabled for deliberation. These amendments include amending the Bill from a blanket ban to a case-by-case assessment of trophies imported into the United Kingdom based on whether they contribute to the conservation of wildlife and human economic upliftment.
For example: Amendment Clause 2(d) states that hunting imports may only be granted if:
“a hunting area where the hunting operator can demonstrate that financial or non-financial benefits of trophy hunting materially contributes to the conservation of the trophy hunted species, including habitat protection, anti-poaching measures, and support for community livelihoods.”
At face value, this appears to be equitable. Ignoring the obvious ethical dispute, if trophy hunting can be proven to benefit the conservation of wildlife and human livelihoods, then perhaps it may be a case to consider. However, the problem in the majority of trophy hunting cases, and in most countries where trophy hunting takes place, the activity not only is wholly unable to benefit wildlife and human communities, but precipitates the opposite.
Botswana, one of the major destinations for trophy hunters, is a particular case in point.
The southern African nation has been promoted by some in the House of Lords as an example of a trophy hunting ‘success.’ So much so that a high-level delegation of government officials from Botswana, including a minister, an ambassador and a wildlife department head of authority were invited to the House of Lords in June 2023 to make a case for the benefits of trophy hunting in their country. Yet, serious questions surround Botswana’s ability to adequately regulate trophy hunting and provide any meaningful benefits for communities living among and alongside wildlife.
Field investigations, in-person interviews and literature, financial audit, international policy document reviews have been undertaken over the course of a year to assess the validity that Botswana can provide meaningful and tangible benefits to its wildlife and people. This is a summary of the results:
- On an international level, the country has been flagged for non-compliance under the Convention on International Trade of Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) due to its failure to submit annual reports, which provide crucial information for validating offtake of elephants for trophies for the international trophy trade. This indicates that the wildlife conservation in Botswana is not adequately managed.
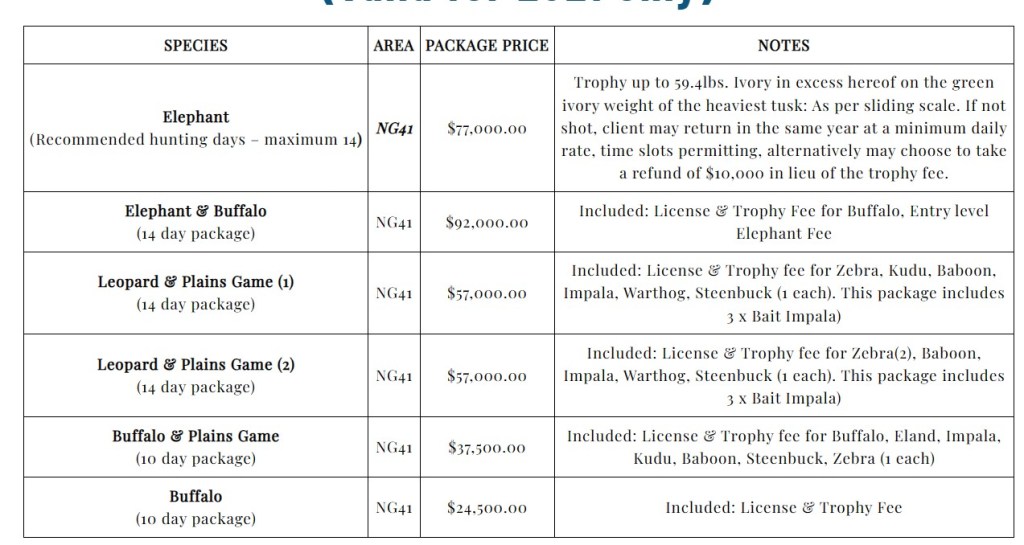
- Hunting quotas are not based on scientific data. A total quota of 356 Elephants and 74 Leopards are on the Wildlife Hunting Quota List for 2023. These figures are regarded as abnormally high. The list also includes Zebra, Buffalo, Ostrich, Wildebeest, Kudu, Eland, Gemsbok, Warthog, Baboon, and Lechwe.
- There is evidence of widespread unethical hunting practices including over-use of already overly high quotas, fraudulent practices, corruption, baiting, and hunting near and within photographic tourism zones. As well as the deployment of aerial support to search for large tuskers and killing Elephant bulls near artificial waterholes.
- Trophy hunting activities in Botswana are forcing communities, which are expected to rely on the proceeds of trophy hunting, into a perpetual cycle of impoverishment and economic disenfranchisement. Trophy hunting obstructs the development of more meaningful activities like photographic tourism while the proceeds from trophy hunting are so miniscule that individual community members are practically receiving nothing.
- There is also widespread evidence of corruption and mismanagement of funds generated by the Community-Based Natural Resource Management (CBNRM) system in areas centred on trophy hunting as the main economic activity. The mismanagement and corruption are directly linked to trophy hunting.
- The current government has revoked scientific research permits of organisations that have been committed to providing peer reviewed scientific data on the conservation status and ecology of Elephants and suppress those that have dared to voice concern over unsustainable and unethical hunting practices.
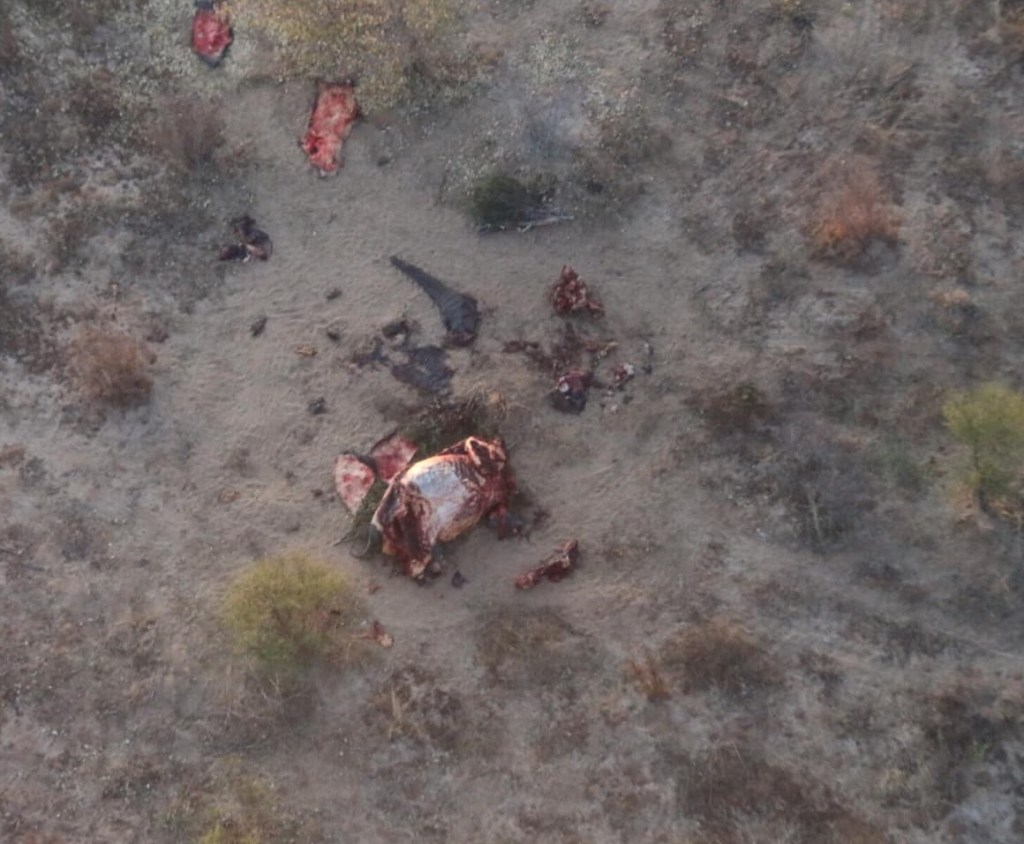

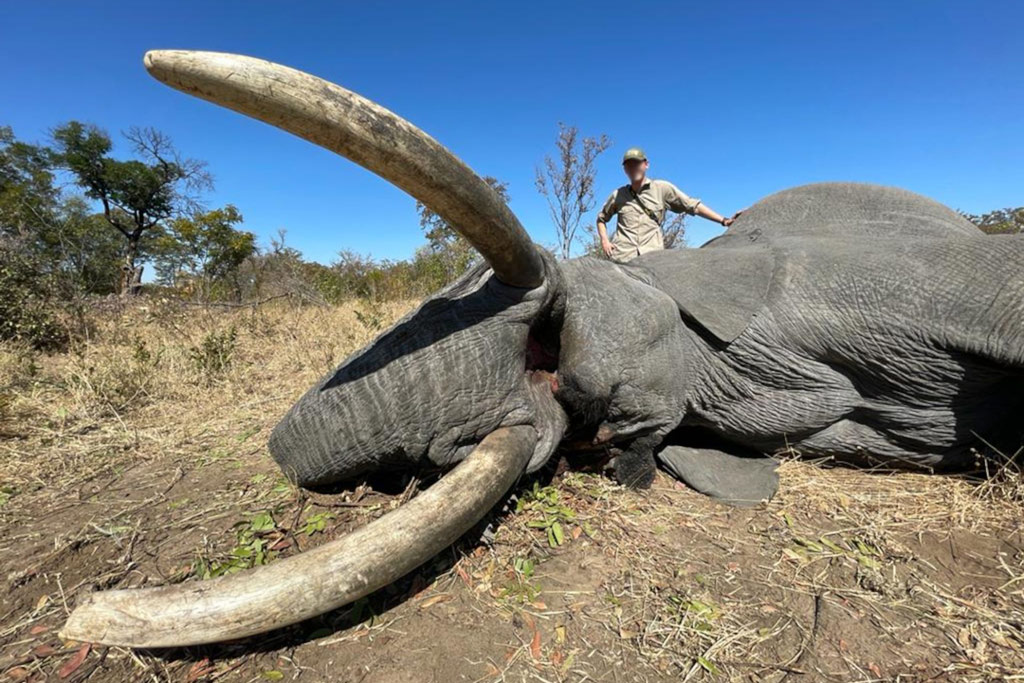
The adult Elephant Bull (above) has been stripped of its body-parts. The trunk has been hacked off. There are large portions of the Elephant’s skin cut off. All four feet have been removed – presumably to make foot / table stools (the Botswana president, Mokgweetsi Masisi, (in)famously gave Elephant foot stools to the presidents of neighbouring countries at an Elephant Management meeting in Kasane in 2019). The tusks and skull have been taken to a taxidermy. These body parts represent the prize – the trophy – that the hunter was after, and which will be displayed on a wall in their home in Europe or America or Asia. There is also some flesh cut off on the flanks of one side, possibly to provide some meat for the trackers and skinners as a ‘tip’.
It has been claimed in Botswana that trophy hunting is only undertaken in ‘marginal’ wilderness areas that are not deemed viable for photographic tourism. It is also claimed that attempts to convert trophy hunting areas not viable for photographic tourism into photographic tourism areas is a challenge. Areas that are deemed not viable for photographic tourism are remoteness, lower densities of wildlife and monotonous natural landscapes. In these spaces, trophy hunting becomes a necessary evil as the sole provider of revenue for remote communities living within and alongside wildlife.
And yet, this Elephant was shot in a hunting concession (NG41) that is neatly wedged between two national parks – Moremi Game Reserve and Chobe National Park. These two parks are globally renowned for photographic tourism and are consequently brimming with tourists wanting to photograph what Botswana showcases best – wildlife. The fact that that this Elephant was shot right in the middle of these tourist hotspots makes a mockery of the claim that trophy hunting in Botswana only takes place in marginal areas.
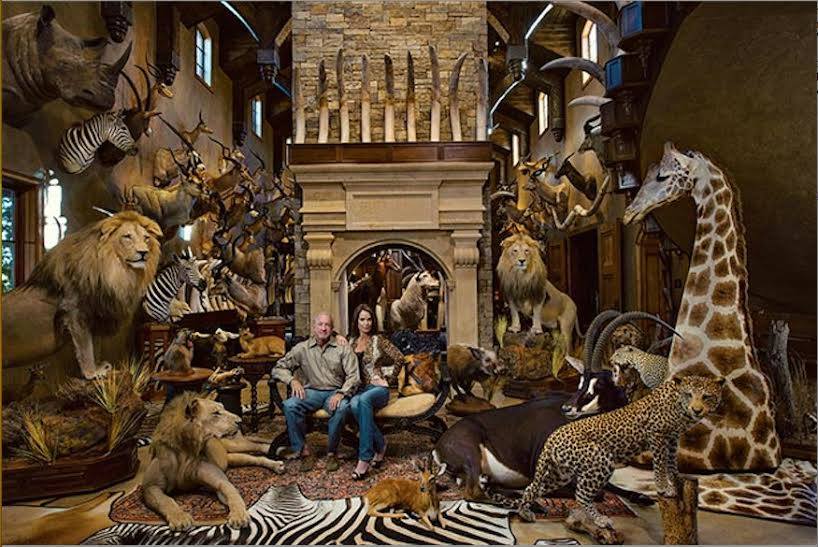

The standard narrative from hunters and their proponents is that trophy hunting is an essential conservation tool that, if conducted ‘ethically’, preserves endangered wildlife and provides revenue for impoverished communities living in marginalised areas where photographic tourism is absent. Yet as this case shows, as they all do, that narrative is a false one. Stripped of its protective fairy-tale veil, the true face of trophy hunting lays bare, a narcissistic bloodlust of a few depraved individuals who care little for ethics, community upliftment or wildlife conservation. ~ Adam Cruise.


WHAT YOU CAN DO TO HELP WILDLIFE:
You can support ‘Protect All Wildlife’ by donating as little as £1 – It only takes a minute but it can last a lifetime for an animal in need. Please donate below.
Everyone who donates will receive a Certificate of Appreciation as a thank you for helping animals in need.

The Mission of Protect All Wildlife is to prevent cruelty and promote the welfare of ALL animals.
We believe EVERY animal should be treated with respect, empathy, and understanding. We raise awareness to protect and conserve wild, captive, companion and farm animals.
It is vital that we protect animals against acts of cruelty, abuse, and neglect by enforcing established animal welfare laws and, when necessary, take action to ensure that those who abuse animals are brought to justice.
Protect All Wildlife are involved in many projects to protect animals’ rights, welfare, and habitats. Money contributed to Protect All Wildlife supports ALL of our worthy programmes and gives us the flexibility to respond to emerging needs. Your donations make our work possible.










