If former Guns & Roses guitarist Slash hadn’t put all his heart and soul into music and becoming one of the world’s greatest rock guitarists, perhaps he would’ve sought a career in zoology?
He is a trustee of the private, non-profit Greater Los Angeles Zoo Association (GLAZA) and shot a commercial for Los Angeles Zoo and Botanical Gardens with veteran actress Betty White to promote their new exhibit The Lair, which displays over 60 species of weird, rare and endangered amphibians, invertebrates and reptiles. He has shot other ads and PSAs before for the zoo.
“I used to not believe in zoos as a concept, but now because there are so many endangered animals; there’s so much poaching,” Slash tells Samaritanmag. “With zoos now, it’s really about conservation. They become safe houses for a lot of species so, I think, now, zoos are really necessary places, not totally about just family entertainment at any cost. It’s about education; it’s about conservation.”
Anyone familiar with Guns N’ Roses, Slash’s former band, knows he used to own snakes — as many as 80, which he got rid of when he became a father. He has been on the cover of Reptiles magazine and even had a band called Slash’s Snakepit post GNR. But he’s actually a lover of all animals.
Slash has been visiting the LA Zoo since the age of 5 and later in childhood went every weekend, sometimes twice. As a touring musician, he often visits the local zoos on his downtime.
in 2011, Slash received the inaugural Tom F. Mankiewicz Leadership Award from GLAZA at the 41st Annual Beastly Ball recognizing his long-time support of the zoo and the welfare of the world’s natural and civic environment (filmmaker Mankiewicz was GLAZA chairman who died in 2010).
The award will recognises his long-time contributions to environmental welfare programs and his support to the LA Zoo and zoos around the world.
GLAZA (Greater Los Angeles Zoo Association) President Connie Morgan declared:
‘Tom [Mankiewicz] advocated opportunities for interaction among our diverse communities and championed the cause of animals and the environment through education and on-the-ground conservation. He strongly believed the Los Angeles Zoo exemplifies both missions as a place where people come together having a good time while learning the importance of saving and protecting wildlife.’
To which Slash responded:
‘The biggest compliment for me is that it’s Tom’s award. I really adored that man. I miss him very much, and that aspect is very special and resonates deeply. Additionally, I profoundly appreciate the implications of the award itself. It’s a fantastic honour.’
But Zoo director John Lewis could not stop there:
‘Slash is a great example of our mission of nurturing wildlife and enriching the human experience. He is a champion for wildlife and conservation and has introduced our mission, his passion, to millions of his fans’.
“I just try to help the zoo,” says Slash of his role as a trustee. “We all on the board support and help the zoo’s best interests. We just try to keep all that together. It’s a pretty big thing. It’s a city-owned zoo and we’re trying to make it a private zoo and there’s just always something going on with that.”

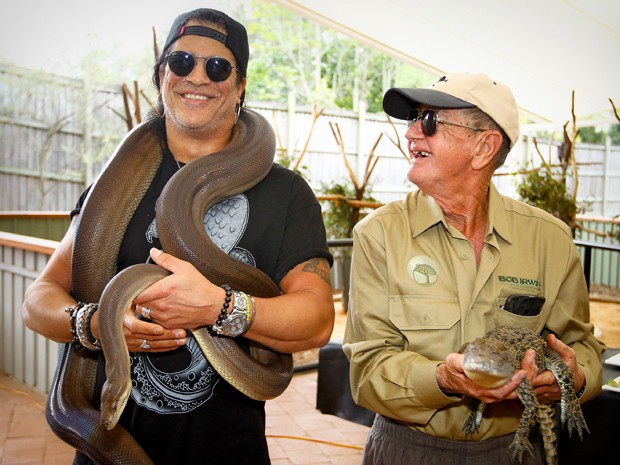
In 2012, while on a trip to Australia, Slash took wildlife warrior Bob Irwin up on an invite, but left the meeting by signing on to aid Irwin’s new conservation initiative.
SLASH loves reptiles. So does Bob. And that’s enough.
A deep affinity for the cold-blooded creatures has forged an unlikely friendship between the legendary Guns N’ Roses guitarist and wildlife warrior Bob Irwin.
Irwin, who is the father of late ‘Crocodile Hunter’ host Steve Irwin, reached out to the guitarist when he learned the tour was coming to Australia, and invited him down to Queensland to visit the crocodiles and snakes.
After lending his support, Irwin returned the favour by urging his followers to catch one of Slash’s performances while he was visiting the country.

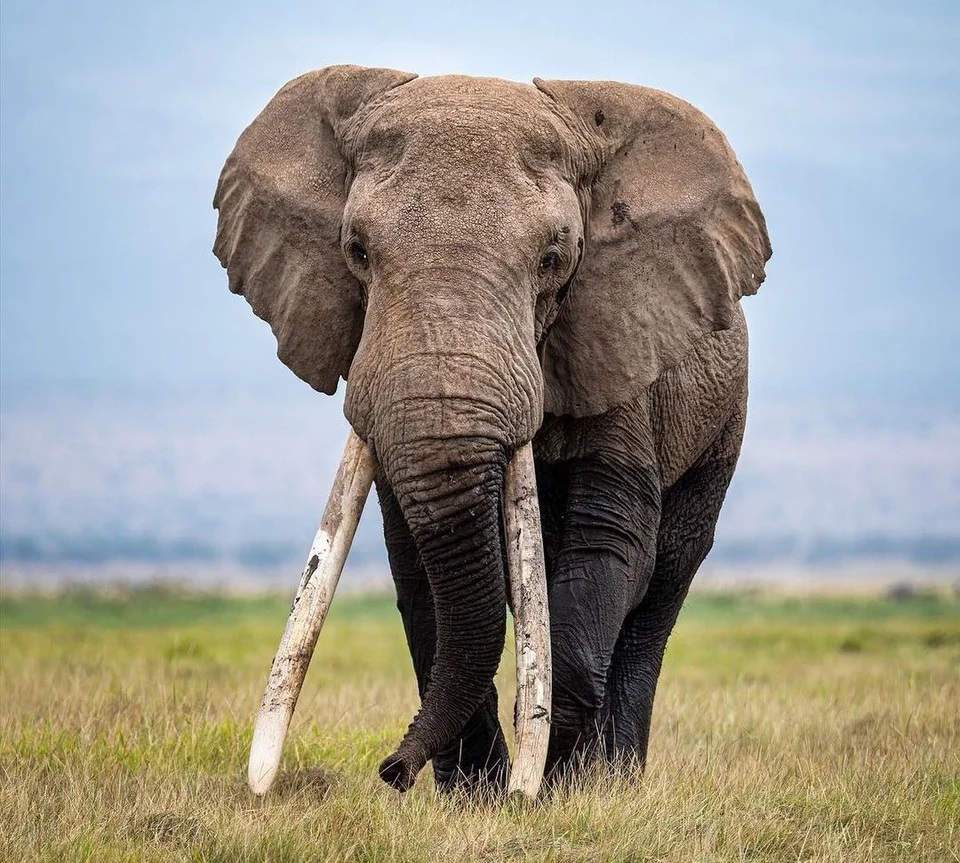
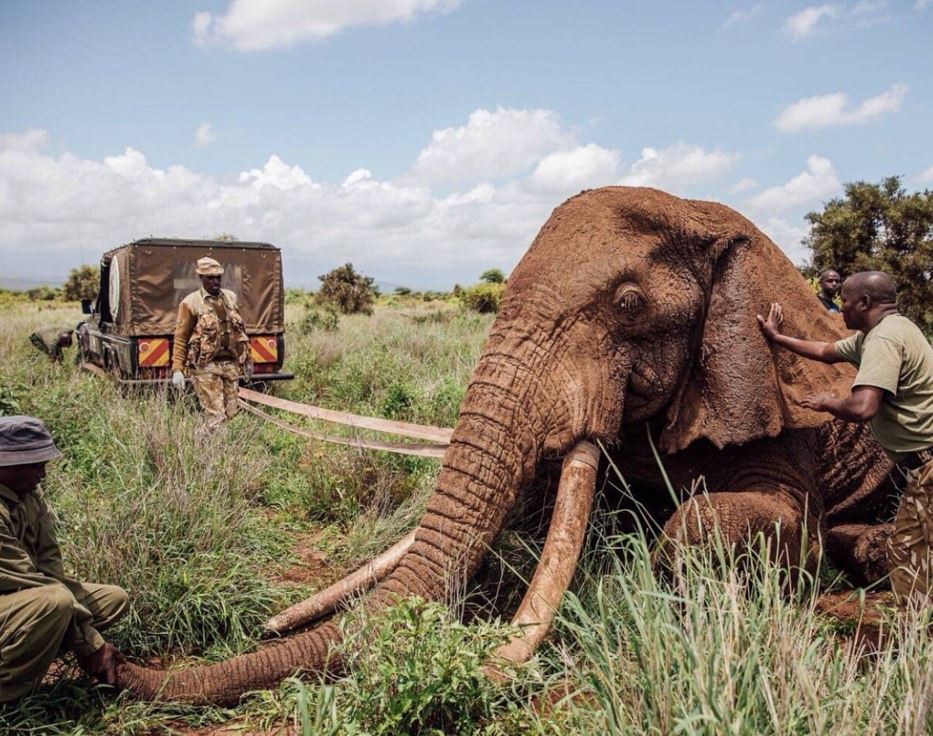
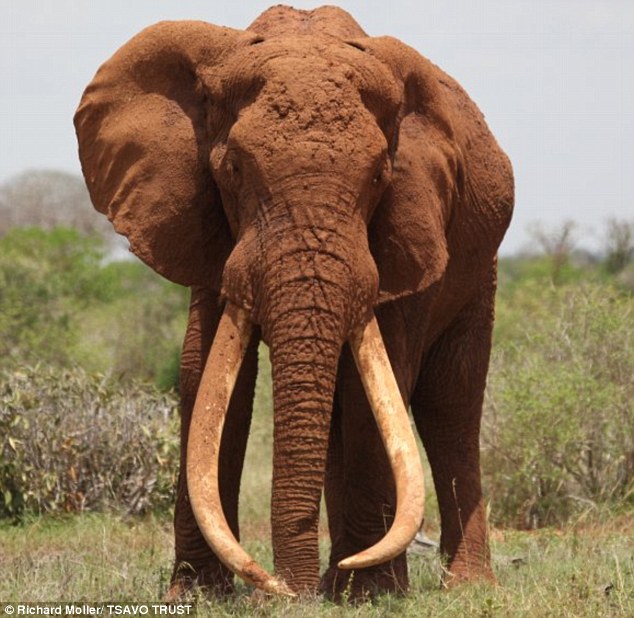
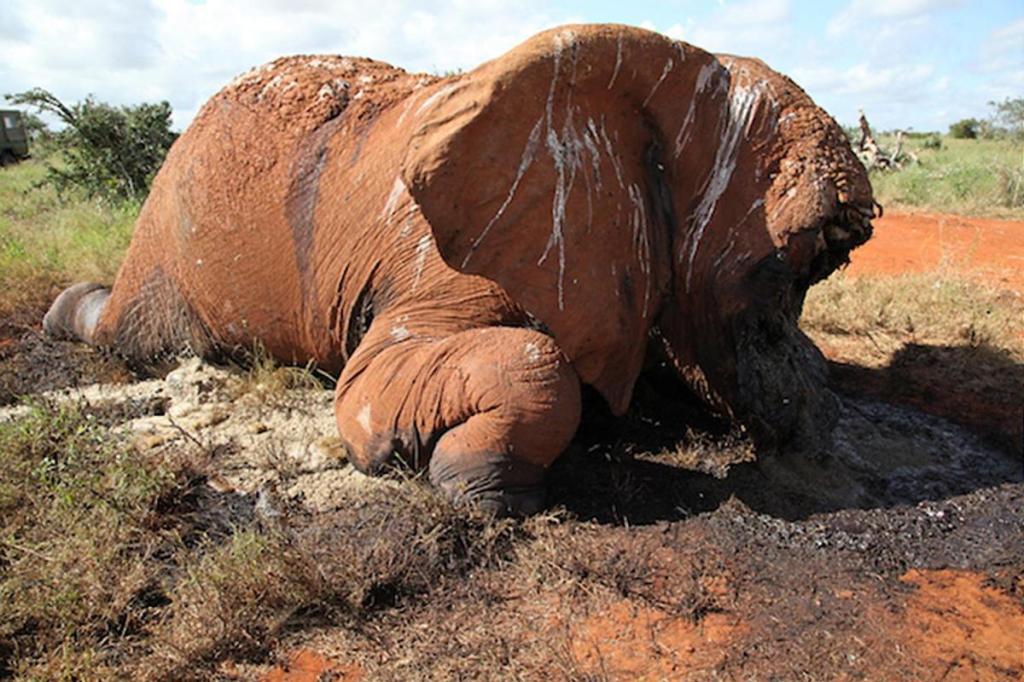
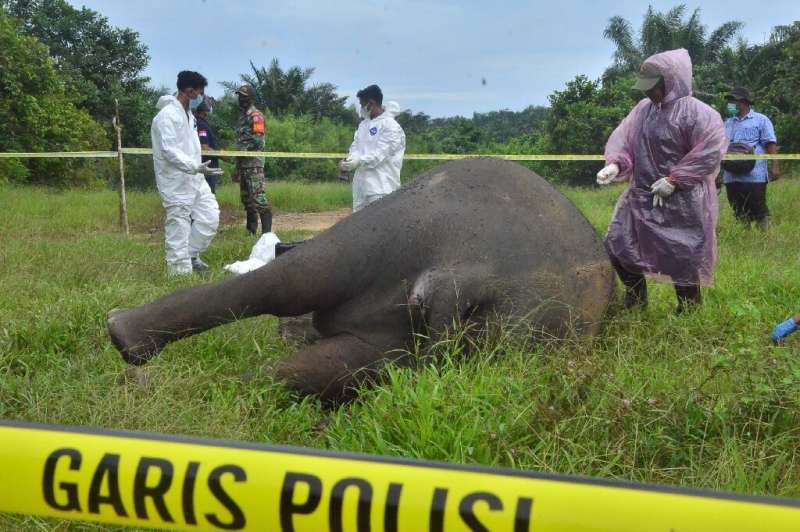
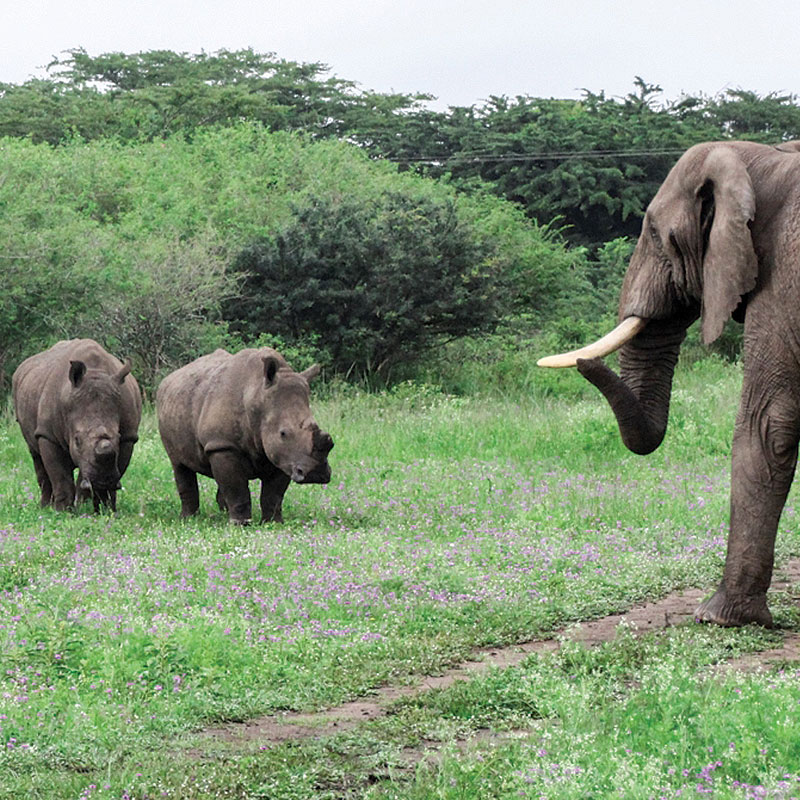
In 2013, Slash performed in South Africa with rock super group Kings of Chaos and spent extra time seeing the local wildlife. Although he had been aware of the diminishing numbers of Elephants in the world, the former Guns N’ Roses guitarist learned on this trip that the situation was becoming increasingly more dire. While poaching rangers had increased their efforts to stop the illegal ivory trade, Slash believed that people needed to be more aware of the situation.
The guitarist also released the “Beneath the Savage Sun” video, which details the illegal ivory trade and tells the story of an Elephant who has lost a loved one from the Elephant’s point of view.
“How many killing seasons can you justify?” he asks. “How many dead and bleeding / only for an ivory lie?
“I was shocked that the poachers still manage to get away with it,” he told Rolling Stone in the above video. “A lot of people don’t know that every time they purchase anything that has even a smidgen of ivory in it, it comes from a dead Elephant. I think if people were more aware of that, it would have a dramatic effect on the whole ivory trade.”
Slash’s singer, Myles Kennedy, was equally affected by the situation. Kennedy wrote the lyrics for what would become “Beneath the Savage Sun,” a doomy hard rocker told from the perspective of an Elephant who witnessed the death of a fellow pachyderm.

Slash made a powerful video for the track – which is featured on the guitarist’s last solo album, 2014’s World on Fire – illustrating the brutality of the ivory trade with written facts, images of both living and murdered Elephants and poachers’ spoils. The video notes that the U.S. is the world’s second-largest consumer of ivory, so Slash hopes the clip serves as a wake-up call.
“We wanted to give the viewer an idea of the atrocities that are going on, to hit them full in the face with it,” says Slash, an animal lover who is on the board at the Los Angeles Zoo and has long been active in animal conservation. “It’s more of an immersive experience. The most important thing is to reach as many people as possible.
“Elephants are so beautiful, intelligent and sensitive,” the guitarist continues. “They have emotions we’re all familiar with. They care for their young. They move in big family groups that live on for generation after generation. They very visibly mourn their dead. When you actually meet Elephants and get to know them a little bit, they have a whole myriad of personalities.” (Slash was previously part of the campaign for Billy the Elephant.)
In addition to educating people about Elephants, Slash has also partnered with the International Fund for Animal Welfare (IFAW), an organization he reached out to personally because he had worked with them in the past and liked how they were “hands on” in their causes.
Jeff Flocken, IFAW’s regional director, North America, has been working with the Obama Administration to draft and implement laws to regulate ivory. “Any legal trade of ivory encourages illegal trade,” he says. “Our laws are riddled with loopholes like Swiss cheese.”
He believes that if the U.S. led by example, real change is possible. “Last November, the U.S. crushed six tons of ivory that was seized illegally here in the U.S., and within months, China crushed 6.1 tons of their own ivory,” he tells Rolling Stone, adding that China is the world’s Number One ivory consumer. “It’s the first time they’ve ever done that. It shows that other countries are watching what we’re doing.”
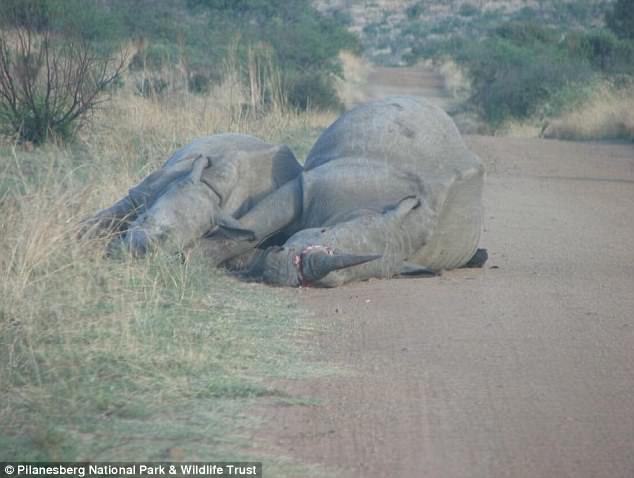
Trade in elephant ivory is driving these amazing animals to extinction; largely at the hands of criminal networks that kill local wildlife rangers and support organized crime, smuggle drugs and transport illegal firearms. They do all this to meet the lucrative demands of consumers in China, the United States and elsewhere, many who don’t even realize that every piece of ivory comes from a dead elephant, but who still value the stuff as jewellery, trinkets, and yes, instruments.
Flocken added that the anti-ivory movement has begun facing opposition from the N.R.A., who want to protect ivory for ornamentation on gun handles, among other causes. Slash says that ivory ornamentation is not necessary and uses musical instruments as an example.
We love our instruments. We know that many of you love your guitars with ivory bridges and pianos with ivory keys, but we need you to think about where things came from and what are your ethics when buying and selling them?” Piano keys don’t have to be ivory,” he says. “It’s not important. And for inlays on guitars and tuning pegs, it’s absolutely not necessary and I won’t use it.” Do we really want to profit off of the extinction of such a beautiful and majestic species?
To prove his point, Slash donated proceeds from the sale of the song to the IFAW and has redesigned his website to provide more information about the ivory trade and serve as a place where people can donate to the organization. Supporters can also donate to the IFAW.
“Donating is great – that’s hugely necessary – but the other thing to do is to stop purchasing ivory,” Slash says. “Do not buy it. I think the more people that stop buying ivory is going to have a significant effect on the Elephant poaching trade.”

The Mission of Protect All Wildlife is to prevent cruelty, promote the welfare of ALL animals EVERYWHERE, and help END animal abuse.
Please support our work by donating ANY amount, large or small. It only takes a minute and your donations make it all possible. Thank you for your support.