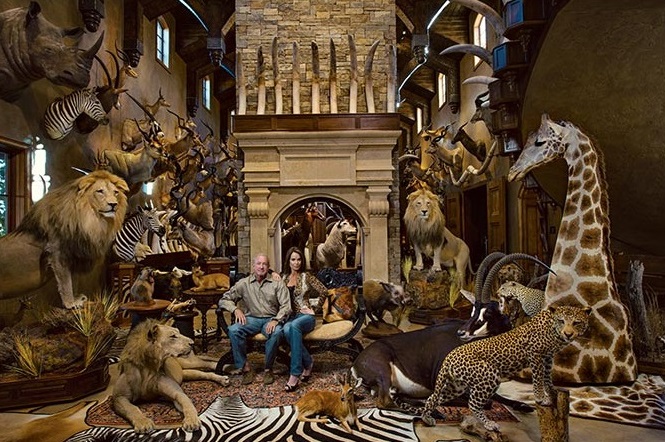
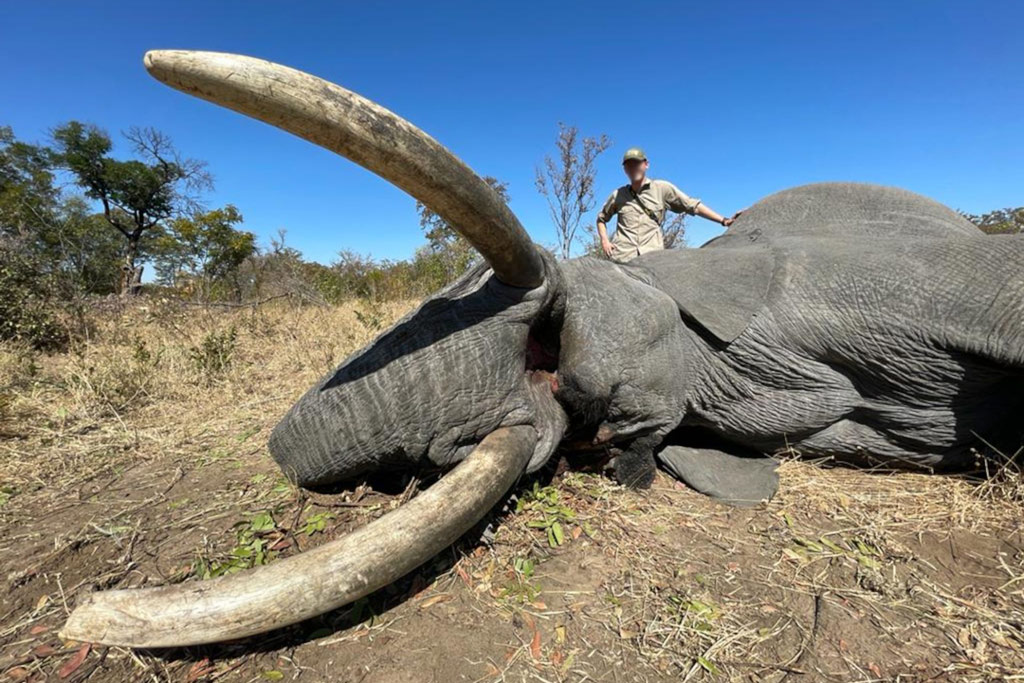
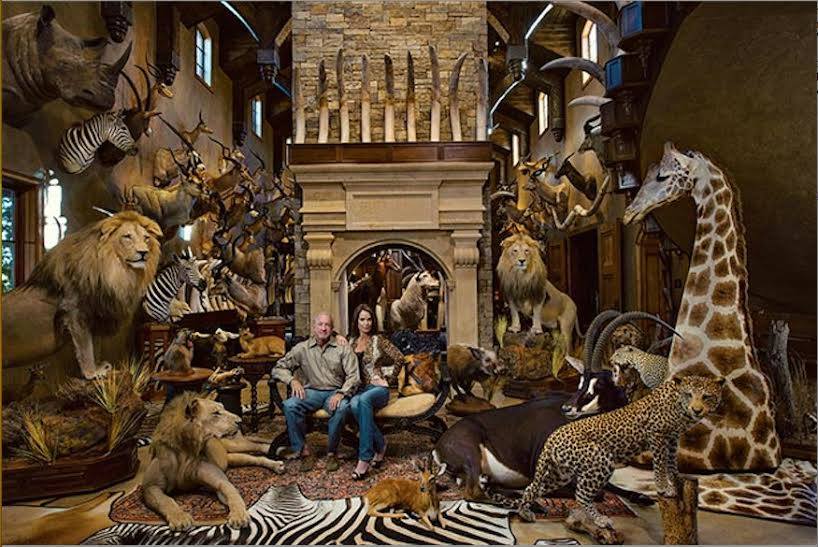
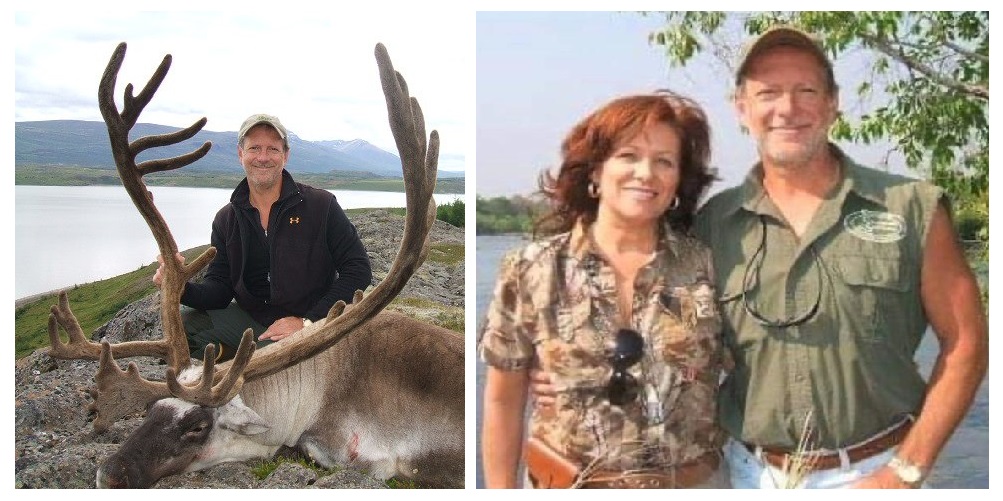
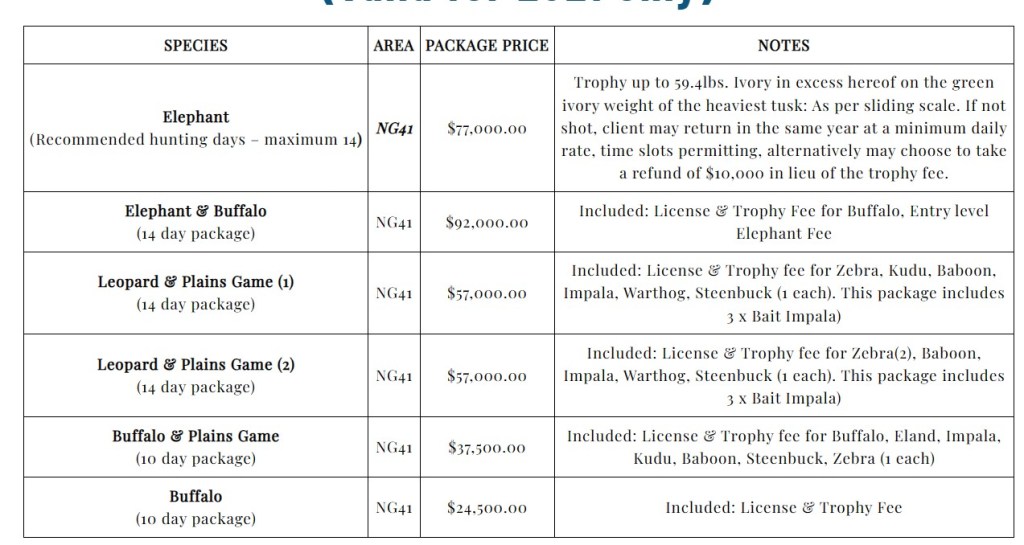
Kerry Krottinger, a wealthy Texas hunter and businessman, has slaughtered so much African wildlife over the years that he amassed a veritable “wall of death” in his Dallas home. The National Geographic portrait depicts him sitting with his wife among the taxidermied bodies of Lions, Rhinos, Cheetah, Giraffes and enough Elephant tusks to open a traditional Chinese hospital.
The British-based charity LionAID, which uploaded the photo to their Facebook page, took a markedly dim view. “This is just one Texas trophy hunter with a ‘love’ of Africa,” they write. “Is it any wonder that Africa’s wildlife is disappearing? Just have a count of the various species displayed. Three Lions? So many Elephant tusks? A Giraffe? A Rhino? Kerry must be one of the leading CONservation hunters on the planet!”
Little is known about Krottinger’s personal life. Aside from being an energy millionaire with multiple companies to his name, he and his wife Libby operate a Gypsy horse farm called Ndugu Ranch. A website about the property had been taken offline, but a cache copy can be viewed here. A Facebook page also associated with the ranch was also taken down. Next to a smiling photo of the pair, Krottinger wrote he named the ranch after the Swahili word for “brother” or “family member,” and that the couple has “a great love for Africa.”
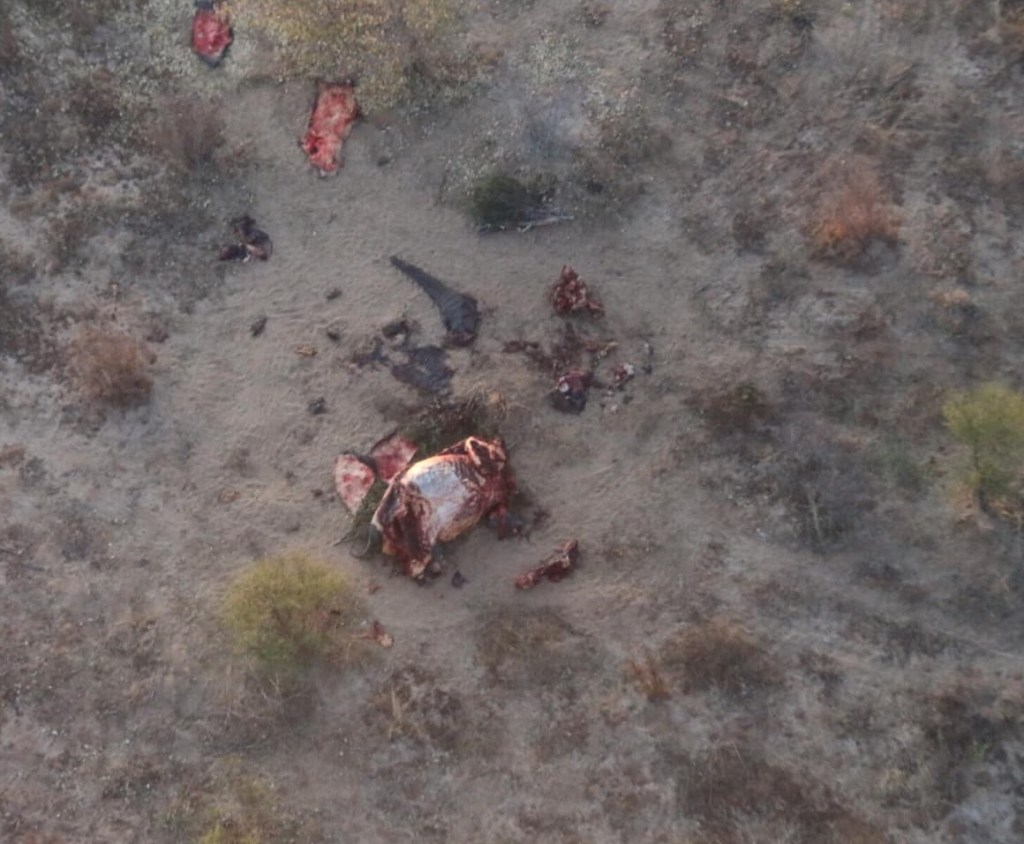
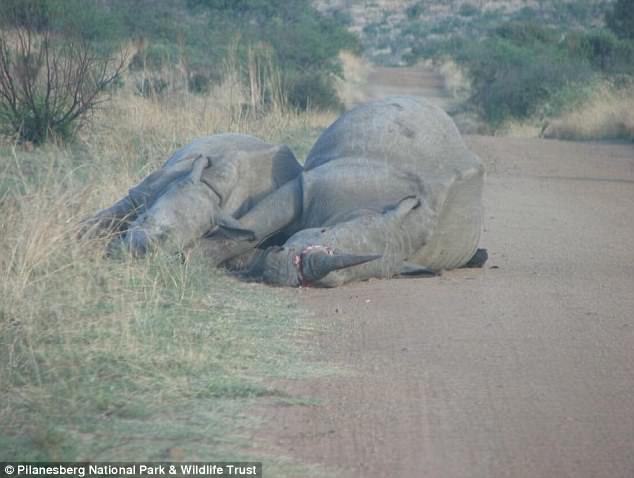
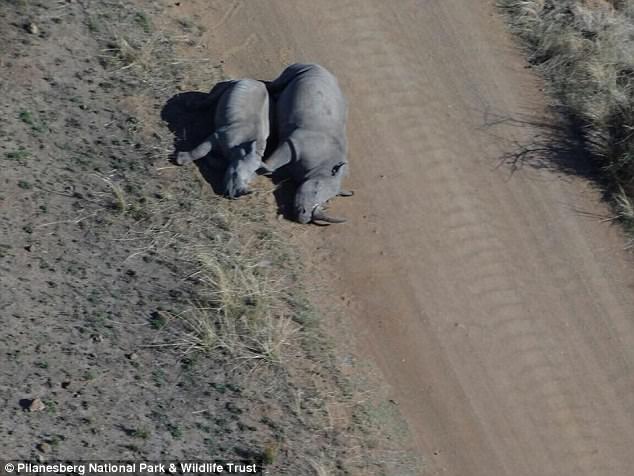
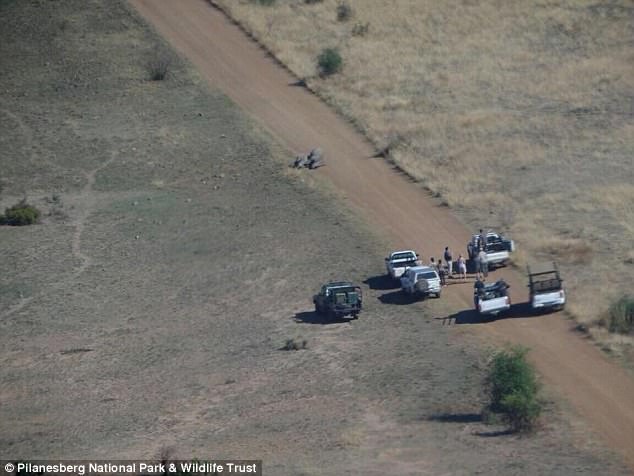
Krottinger’s kingly haul of animal carcasses was acquired through what’s known as “conservation hunting,” a practice that is supposedly designed to protect species by allowing people to hunt animals for a high fee that’s then to be used for other conservation efforts.
Far from poachers, conservations hunters — and the websites that promote them — see themselves as environmentalists. LionAID’s director Pieter Kat said the whole premise was nonsense.
“Conservation hunting is a complete myth,” he told Mic. “If conservation hunting had been effective, Cecil the Lion would not have to have been poached out of a national park, because conservation hunting would have maintained a viable and sustainable Lion population within their own trophy hunting concession.” According to Kat, steep fees like the more than $50,000 Palmer paid to kill Cecil typically end up in the pockets of tour operators. “Sustainable hunting does not sustain anything,” he said.
PETA president Ingrid Newkirk was blunter still. “The idea of killing animals to ‘protect’ their species is like having 5-year-olds build a child-labor museum,” she said in a statement to Mic. “True conservationists are the people who pay to keep animals alive through highly lucrative eco-tourism, not the power-hungry people who pay for the cheap thrill of taking magnificent animals’ lives and putting their heads on a wall.”
On Twitter, the response was one of almost universal disgust, with the photo generating near Cecil-levels of rage.
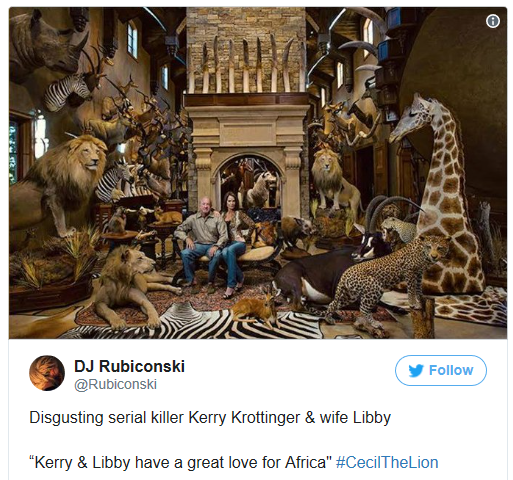




Kat was unapologetic about the Krottinger-shaming on LionAID’s Facebook page. “What we were trying to do there is to alert people to the fact that trophy hunters have this sort of enjoyment of their activity, and what we would like to expose to people is these sorts of people belong in the 19th century,” he said.

WHAT YOU CAN DO TO HELP ANIMALS IN NEED
You can support our work by donating as little as £5 – It only takes a minute but it can last a lifetime for an animal in need.
PLEASE DONATE HERE
PLEASE HELP ANIMALS IN NEED
Everyone who donates will receive a Certificate of Appreciation as a thank you for helping animals in need.

The Mission of Protect All Wildlife is to prevent cruelty and promote the welfare of ALL animals.
We believe EVERY animal should be treated with respect, empathy, and understanding. We raise awareness to protect and conserve wild, captive, companion and farm animals.
It is vital that we protect animals against acts of cruelty, abuse, and neglect by enforcing established animal welfare laws and, when necessary, take action to ensure that those who abuse animals are brought to justice.
Protect All Wildlife are involved in many projects to protect animals’ rights, welfare, and habitats. Money contributed to Protect All Wildlife supports ALL of our worthy programmes and gives us the flexibility to respond to emerging needs. Your donations make our work possible.