Here, Andy Davidson lists the hard-hitting facts, revealing what zoos really spend their money on, and how you’re better off spending yours elsewhere if you care about conservation.
If you’re planning to a visit a zoo this weekend, ask yourself this question. How much of your ticket fee is being used for conservation? Let’s say you pay £15 for your ticket. You may be surprised to hear that the answer is as little as 45p to £1.
Zoo expenditure is vastly different to the expenditure of conservation organisations based in the wild. For example, Chester Zoo spent £40 million on the construction of ‘the islands’, an expansion of more enclosures to the zoo site. Other Western zoos over a ten-year period have spent £400 million on updating enclosures for a mere 200 elephants.
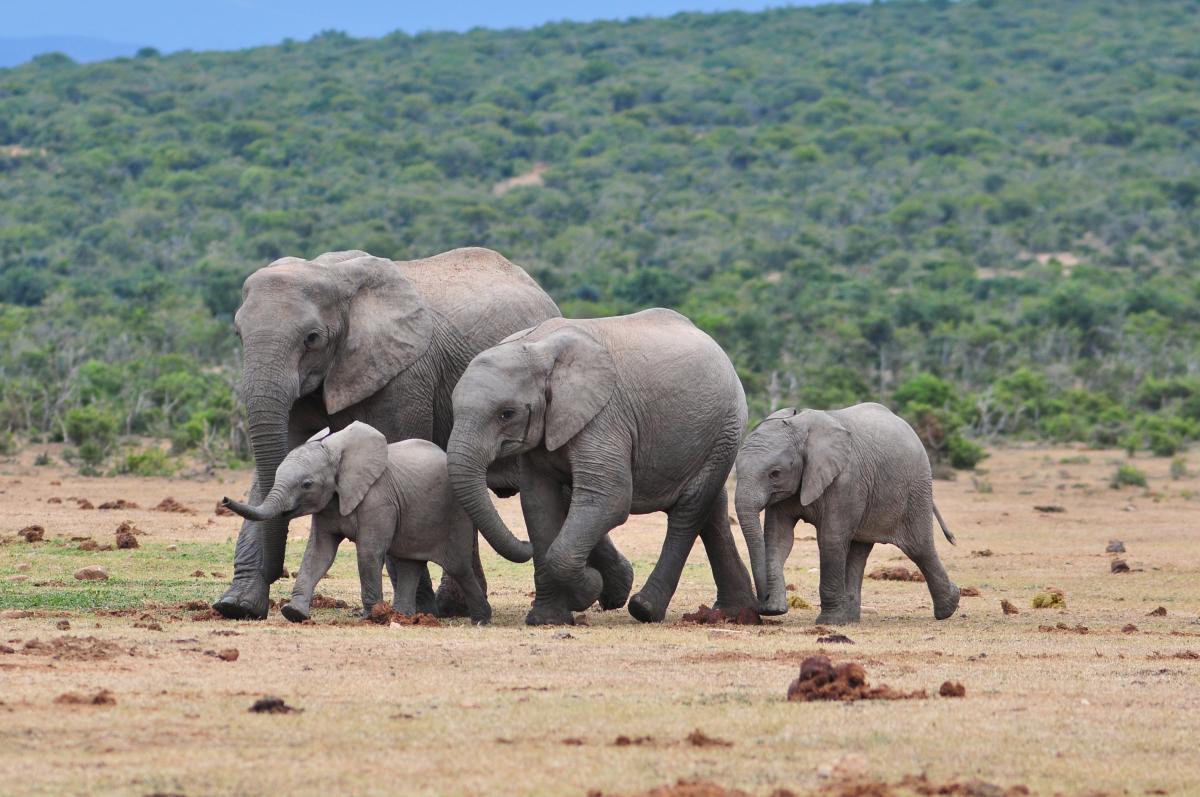

The Kenya Wildlife Service (KWS) and South African National Parks are conservation organisations that protect animals in their natural habitats. KWS has an annual budget of £13-14 million with which they protect 2.6 million hectares of that country’s National Parks. On that land are 33,000 Elephants, 2200 Lions and many vitally important habitats that are home to thousands of species of both plant and animal. The annual budget for the South African National Parks is £58 million and this consists of 19 national parks which make up 6% of the total land of South Africa. Just one of these parks houses 600 elephants.
The money used by Western zoos to update elephant enclosures for 200 Elephants could have kept Kenya Wildlife Service going for 14 to 15 years.
Sound shocking? It is. That’s why the chief consultant to the UN Great Ape Survival Project said he was uneasy at the mismatch between lavish spending at zoos and the scarcity of resources available for conserving threatened species in the wild.
Where Is Your Money Going?
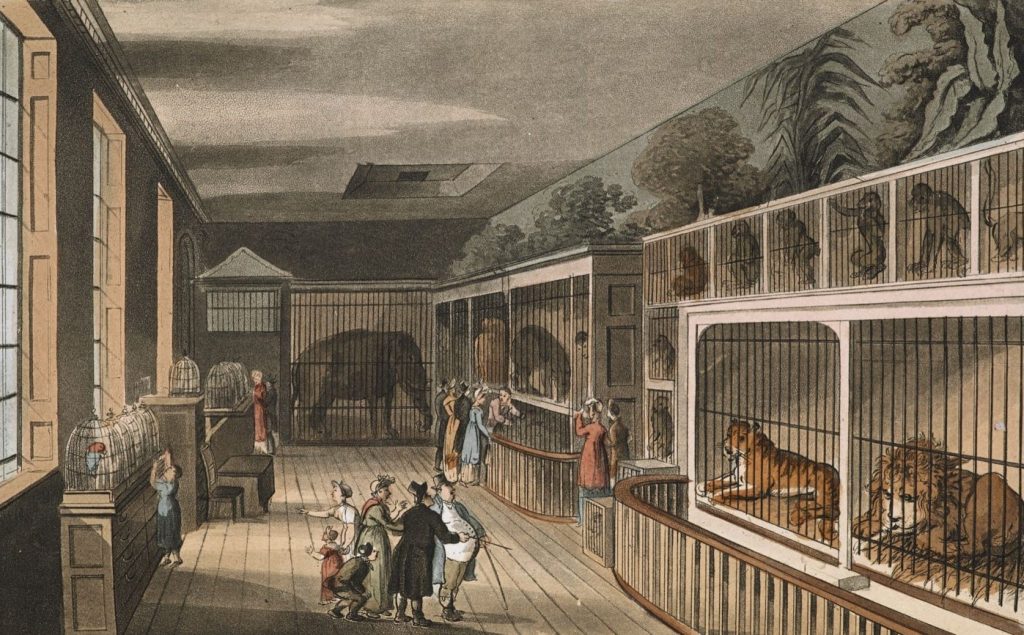
Since the 1800s, the zoo has not fundamentally changed. Well known and entertaining animals such as Elephants, Chimps and Giraffes are front and centre and baby animals give zoos a boost in visitors.
The main driver for zoos is boosting public visitation, a goal that has far reaching implications into all zoo management decisions. Conservation, research and education are not their primary goals, making it impossible to term zoos as research or education organisations. In fact, zoos are places of entertainment, where animal welfare is governed by financial feasibility and entertainment value.
90% of species encaged by European zoos are not threatened from extinction. Over 90% of zoo animals are born in captivity. These animals are then paired across zoos to ensure genetic diversity. Gender cannot be predicted and genes are sometimes over represented leading to what the zoos call a ‘surplus of animals’. 3000-5000 of these animals in European zoos are killed each year. On the 8th of February 2014, Copenhagen Zoo (in)famously killed Marius, a healthy 18-month-old male Giraffe.
Afterward, zoo officials performed a three-hour-long demonstration of how to butcher a giraffe before a large crowd of visitors, including many children. The meat was then fed to the zoo’s four Lions. The four Lions, including two young Lions, were killed to make way for a new male. The Giraffe was killed because she could not produce anymore young.

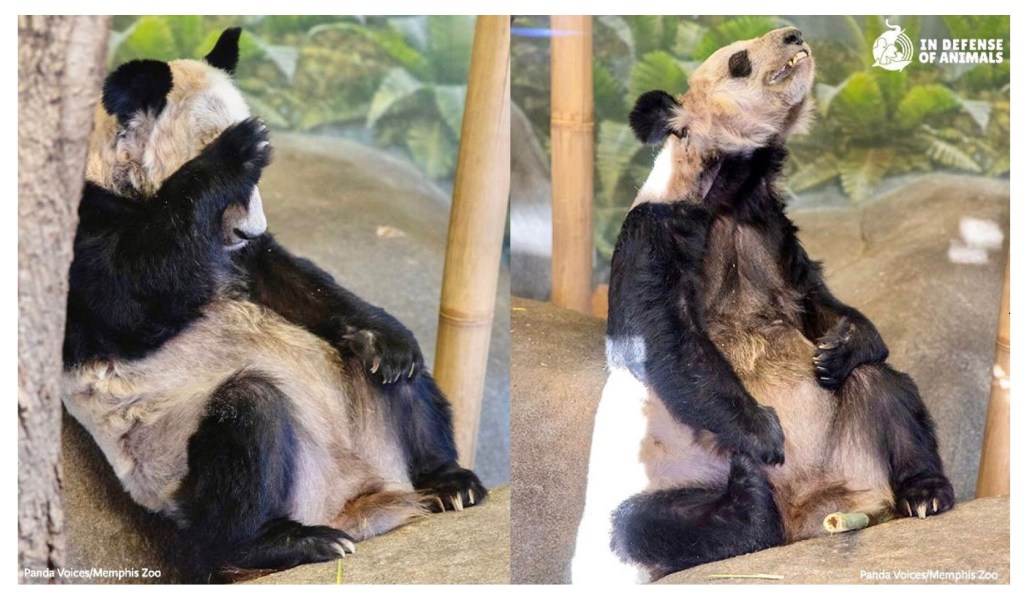
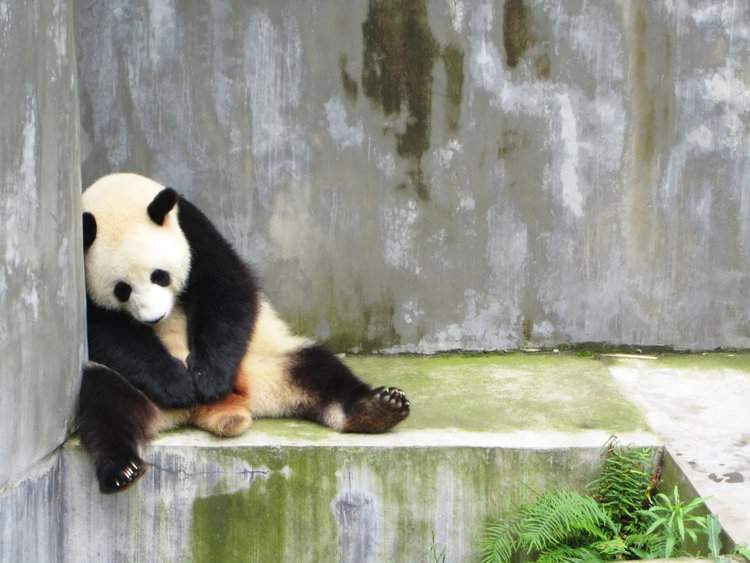
Even for threatened species such as Pandas, breeding campaigns rarely work. 400 Pandas have been bred by zoos, yet only five have been released into the wild: three survived. It’s not hard to see that captive breeding is not feasible. Animals not brought up in the wild are less likely to survive there if reintroduced. For example, captive populations of Red Junglefowl (wild ancestors of chickens) differ significantly in response to predators after just a handful of generations in captivity. And, a 2008 study by the University of Exeter found that the odds of animals such as Tigers and Wolves surviving freedom is only 33 percent. Animals in captivity do not usually have the natural behaviours needed for success in the wild.
But it’s not just endangered species that are being bred. A 2014 analysis of the European Endangered Species Breeding Programmes, conducted by the European Association of Zoos and Aquaria, showed that half of the animals being bred were not classed as endangered in the wild, while 25% were not threatened at all. In fact, all zoos only accommodate a tiny fraction of the 22,000 + species threatened with extinction.
With only 3% of budgets being spent on conversation projects, we can see why wildlife continues to disappear. Zoos show little interest in tackling the root causes of wildlife destruction. Species-rich habitats are being converted to pasture and feed crops as the human appetite for meat swells. Many of the places expected to see the greatest shift in land use from forest to livestock are in 15 ‘megadiverse’ countries, which harbour the largest number of species. As wildlife disappears, zoos ignore the problem. Instead, they contribute to it by feeding millions of customers meat.
The Education Myth
Zoos rebranded in the 1970s as the public became informed to the suffering of zoo animals. UK legislation in the form of 1981 Zoo Licensing Act forced zoos to promote ‘public education and awareness in relation to conservation’. Advocates will say zoos inspire the next generation of conservationists.
This has been categorically debunked by a number of studies, while little information is required to meet the standards of legislation. A 2014 academic study in the Conservation Biology Journal surveyed 2800 children following visits to London Zoo. 62% of the 2800 children were deemed to show no change in learning or, worse, experienced negative learning during their trip to the zoo. It was concluded that the zoo’s impact on children’s belief in their ability to actively do something about conservation was ‘weak’.

Do children need to see the animals up close to learn about them? Many children seem to have an encyclopedic knowledge about dinosaurs, far more so than Lions and Tigers. Perhaps the general public wish to see exotic animals up close as we attach closeness to care. But why, then, do they tap on the windows and show disappointment when the Lions are asleep? This is a misplaced, harmful interest, surely.
In reality there is nothing sufficient in the mainstream that educates the public about animals and their conservation. Zoos, school, television – they all fail in this respect. The evidence is very clear: the World Wildlife Fund report that the planet’s fish, bird, mammal and reptile populations plunged 52 per cent from 1970 to 2010. That’s a stunning 52% of all fish, bird, mammal and reptile life lost in 40 years.
Human encroachment is destroying wildlife, but zoos do not consider that information entertaining and, as mentioned, entertainment is the only real driver of ticket sales. Paul Boyle, senior vice president for conservation and education at the Association of Zoos and Aquariums, says “People leave their homes, and the intent is not to save animals in Africa—it’s to have a family outing.”
The Imprisonment Of Animals
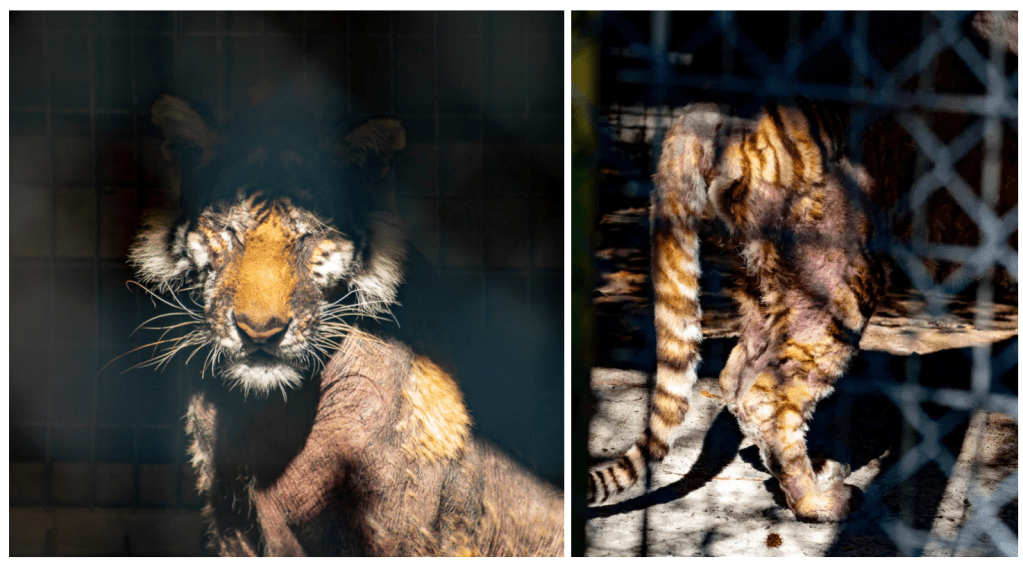
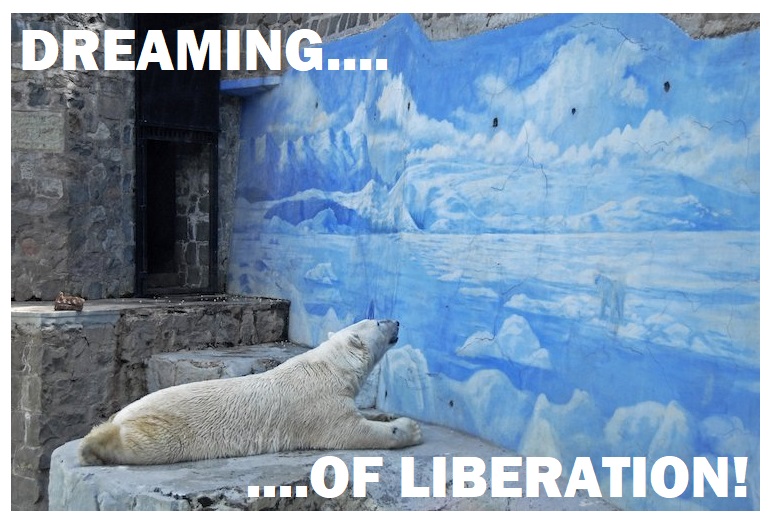
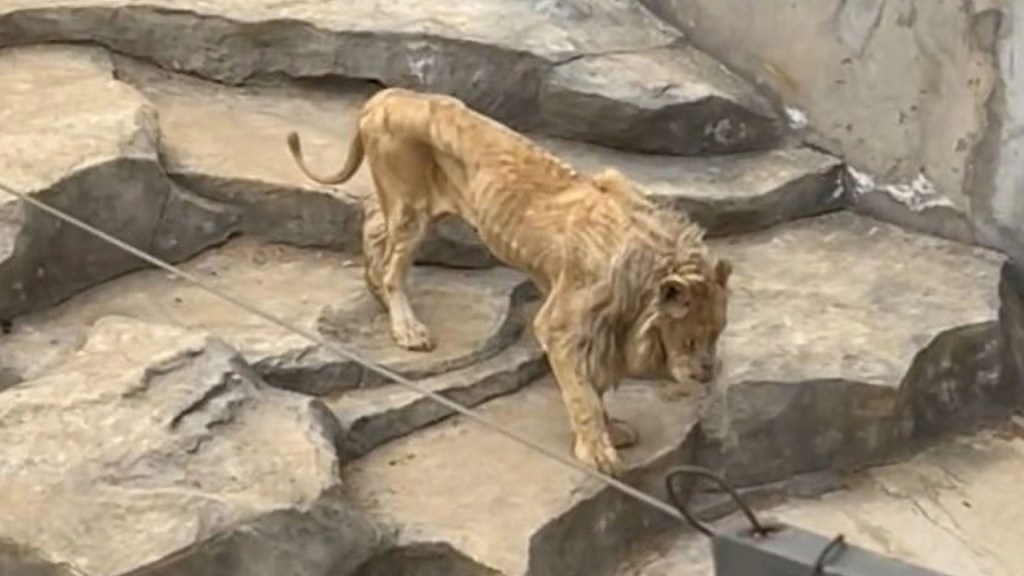
An Oxford University study based over four decades of observing animals in captivity and in the wild found that animals such as Polar Bears, Lions, Tigers, Cheetahs show the most evidence of stress and/or psychological dysfunction in captivity. In the same study, 80% of carnivores show abnormal repetitive behaviour. This is a major problem for zoos as these animals are the most popular with visitors.
There are approximately 3200 Tigers left in the wild. In the United States alone, there are over 5000 Tigers in captivity. This is not the result of successful breeding programmes. These Tigers are being born in captivity and they die in captivity. They are the star attraction. It’s hard to imagine a zoo without a Tiger. One particular zoo in the US houses dozens of Tigers. They let visitors handle cubs and have their picture taken while talking up their conservation programmes, despite the fact that their average Tiger enclosure is about 18,000 times smaller than the animals’ natural roaming range. It is simply impossible for these poor Tigers to express instinctive behaviour.

In two extensive studies, it was found that the lifespan of Elephants is more than halved by living in zoos. A government-funded study of Elephants in UK zoos found that 54% of the Elephants showed behavioural problems during the daytime. In 2016 18 African Elephants, a species designated as threatened within their natural habitats in Swaziland, were captured and transported to three zoos in the US to entertain the public there.
Despite the best intentions of zoo employees to create a happy environment for an animal, zoos are fundamentally unable to recreate the wild setting. Cheetahs cannot run at maximum speed, Elephants cannot walk hundreds of miles (except in circles), birds cannot migrate and fly long distances. Animals are unable to hunt, choose who to spend time with and find their suitable home. Another problem is privacy and noise levels. Human interaction is not normal and constant noise can cause problems. Animals often become depressed and obsessive.
Sometimes zoos are nothing but cages on concrete. Here in the UK, zoos have higher welfare standards, yet its employees and its visitors are still blissfully ignorant to the damage we cause to them. Zoos are well-versed in spreading misinformation and exaggerating the small areas of conservation they achieve to placate the public, ensuring visitor numbers stay high.
Today, the decisions relating to the conservation of animals fall under the power of Western organisations and trusts, not with local communities in Africa or the Amazon. So not only does the money firmly stay within the West, but so does the decision making process. Wildlife can only be saved by empowering their protection in their natural habitats.
If you really care about putting an end to poaching, saving wildlife and keeping wild animals where they belong then pound for pound, your donation should be going to conservation organisations that protect animals in their natural habitats. You won’t receive anything in return and you will have to find somewhere else to visit on your Saturdays, BUT you will be directly saving wild animals. They are the FUTURE: zoos are the PAST.
An Original Article By Andy Davidson, Vegan Society.

WHAT YOU CAN DO TO HELP WILDLIFE
You can support ‘Protect All Wildlife’ many projects by donating as little as £5 – It only takes a minute but it can last a lifetime for an animal in need. Please donate below.
Donate Here: Please Help Animals In Need
Everyone who donates will receive a Certificate of Appreciation as a thank you for helping animals in need.

The Mission of Protect All Wildlife is to prevent cruelty and promote the welfare of ALL animals.
We believe EVERY animal should be treated with respect, empathy, and understanding. We raise awareness to protect and conserve wild, captive, companion and farm animals.
It is vital that we protect animals against acts of cruelty, abuse, and neglect by enforcing established animal welfare laws and, when necessary, take action to ensure that those who abuse animals are brought to justice.
Protect All Wildlife are involved in many projects to protect animals’ rights, welfare, and habitats. Money contributed to Protect All Wildlife supports ALL of our worthy programmes and gives us the flexibility to respond to emerging needs. Your donations make our work possible.